如何区别钢套钢直埋保温管的材料呢
钢材的定义:钢材是铸钢件、板坯或钢材历经工作压力生产加工做成大家所要求的各种各样外观设计、规格和特性的材料。钢材是国家创建和进行四化不可或缺的关键物资供应,运用广泛、类型多种多样,根据横断面外观设计的不一样、钢材一般分成铝型材、板才、管件和金属制造四大类、以便有利于机构钢材的消費、订购提供和做好经营管理工作中


公司扎根水泥制品行业多年,对市政配套水泥制品的研发、设计、生产拥有成熟的经验;并拥有—批管理经验丰富、专业技术强的队伍。

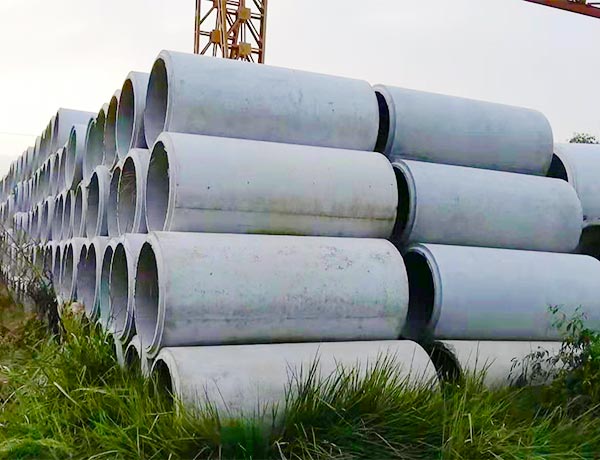
公司主营水泥涵管、混凝土排水管、钢筋混凝土承插管、钢筋混泥土顶管及各种水泥制品,可广泛应用于建筑、桥梁、市政等行业领域!

我公司拥有专门的生产基地,混凝土排水管及水泥涵管供货充足!同时我公司还拥有自己的运输团队,以及物流快递合作伙伴,到货及时,可实现快速交付。


公司拥有7*24小时在线客服,可及时响应解决您的疑惑,并对钢筋混泥土顶管、混凝土承插管等订单实时进行跟踪反馈,让您真正售后无忧!


主营水泥涵管、混凝土排水管、钢筋混凝土承插管、钢筋混泥土顶管等各类水泥制品
咨询热线:134-5210-3890





08/13
钢材的定义:钢材是铸钢件、板坯或钢材历经工作压力生产加工做成大家所要求的各种各样外观设计、规格和特性的材料。钢材是国家创建和进行四化不可或缺的关键物资供应,运用广泛、类型多种多样,根据横断面外观设计的不一样、钢材一般分成铝型材、板才、管件和金属制造四大类、以便有利于机构钢材的消費、订购提供和做好经营管理工作中

01/07
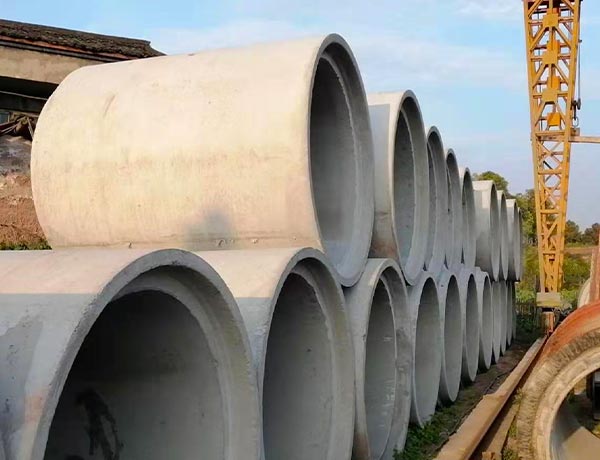
尽管现在管材品种很多,如铸铁管、球墨铸铁管、UPUC管、PE管、玻璃钢夹砂管等,而钢筋混凝土管材,尤其是口径较大的钢筋混凝土管材,仍然是铺设排水管道使用较多的管材

01/07
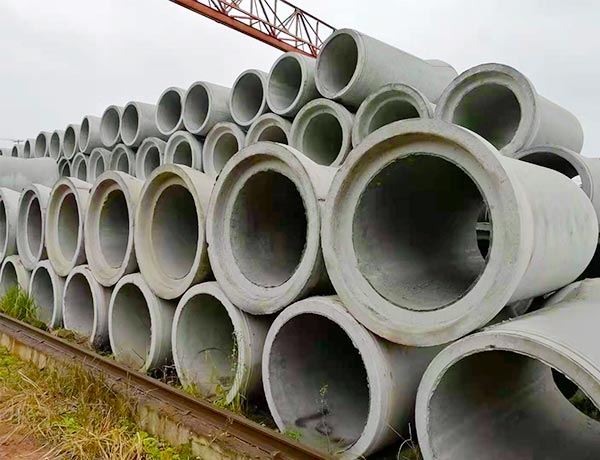
19世纪下半期开始,钢筋混凝土作为结构材料在工业文明的潮流下广泛得到应用,由于其本身的材料特性比其他结构材料更优越,因此在房屋建筑和土木工程中得到了空前的应用和发展,然后相继在材料、设计方法、制作工艺以及施工技术等方面也大显身手。

01/07
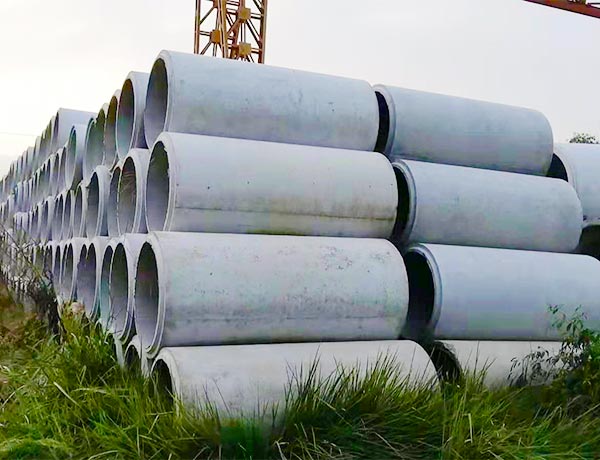
钢筋混凝土排水管的性能优势:钢筋混凝土排水管有磨损力的固体如灰尘、粉末、纤维、屑片和颗粒,气体和液体环境,极度抗磨损且底层有钢丝加强管子强度,或是不加钢丝

03/12
采用离心养护成型工艺制造的电杆,与其他类型电杆相比,在结构性能、生产效率、成本控制等方面具有显著优势: 结构性能优势

02/18
构成:主要由钢筋和混凝土组成。钢筋作为骨架,承担管道受外压时产生的拉力,提高管道的抗裂和承载能力;混凝土包裹钢筋,形成密封的管状结构,起到抗压、防渗和保护钢筋的作用。

01/28
防腐原理:水泥砂浆本身具有一定的碱性,能在金属管道内壁形成一个碱性环境,使金属表面形成钝化膜,阻止金属的进一步腐蚀。同时,水泥砂浆防护层可以隔离管道内壁与输送介质的直接接触,阻挡水中的溶解氧、氯离子等腐蚀性物质对金属管道的侵蚀,起到物理防护的作用。

01/17
可采用水泥浆或环氧树脂胶等材料进行表面封闭处理。将水泥浆或环氧树脂胶均匀地涂抹在裂缝表面,涂抹厚度以覆盖裂缝并略高于周围表面为宜。涂抹后,让其自然干燥或按照材料说明进行适当的干燥处理,这样可以防止外界水分、空气等通过裂缝进一步侵蚀水泥管内部,同时也能在一定程度上增强裂缝部位的强度。
